What if your plate held the key to better mood, energy, and weight control? Tiny chemical messengers in your body hormones influence nearly every aspect of your well being.
Yet modern lifestyles often disrupt their delicate equilibrium, leaving many struggling with unexplained fatigue or stubborn weight changes.
These powerful regulators control appetite, stress responses, and even how your body stores energy. Research shows that processed foods and inactive routines can alter their production. The good news? Strategic nutrition choices create a foundation for optimal function.
Nearly 80% of adults experience noticeable shifts in energy or metabolism due to environmental factors. While genetics play a role everyday meals offer surprising leverage. Specific nutrients act like tuning forks, helping reset your body’s natural rhythms without extreme measures.
Key Takeaways
- Hormones act as messengers influencing weight mood, and energy levels
- Modern eating patterns may disrupt natural production cycles
- Targeted nutrition supports the body’s self regulation mechanisms
- Food choices directly impact metabolic and emotional resilience
- Practical adjustments often outperform restrictive protocols
Understanding Hormonal Balance
Your body operates like a precision network with hormones acting as messengers that coordinate everything from calorie burning to emotional responses. These chemicals work in sync ensuring your systems adapt to daily demands while maintaining stability.

Chemical Messengers at Work
Key regulators like insulin manage blood sugar, while cortisol adjusts your stress reactions. Thyroid hormones set your metabolic pace, and sex hormones like estrogen influence fat distribution. Even slight shifts in these levels can trigger chain reactions.
Hormones don’t operate in isolation they’re part of an intricate web that responds to both internal needs and external pressures.
Health Impacts of Fluctuations
When one hormone falters, others compensate. Elevated cortisol might suppress thyroid function, while insulin resistance often accompanies estrogen changes. These disruptions manifest as:
| Hormone | Primary Role | Imbalance Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Insulin | Glucose regulation | Weight gain, cravings |
| Cortisol | Stress management | Fatigue sleep issues |
| Thyroid T3/T4 | Metabolic rate control | Temperature sensitivity |
Natural life stages like growth phases or reproductive cycles require different hormonal support. Recognizing these patterns helps identify when targeted nutrition becomes most effective for maintaining equilibrium.
Key Principles of a Nutritious Diet for Hormone Regulation
The foods you consume daily act as tools your system uses to maintain equilibrium. Prioritizing specific nutrients optimizes communication between cells while supporting natural regulatory processes.

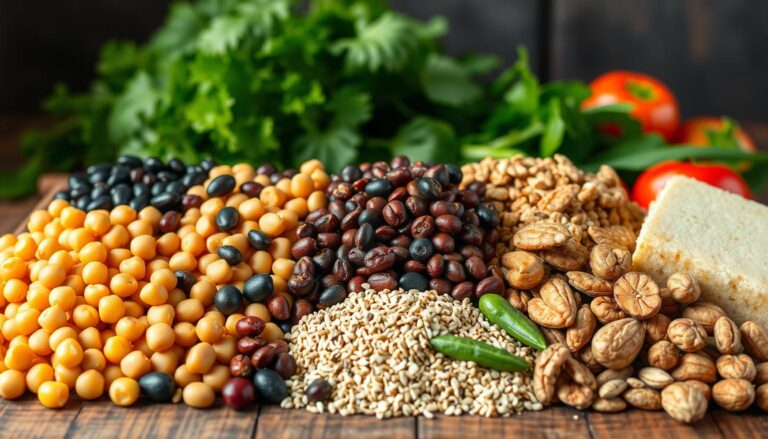
Importance of Protein and Fiber
Protein supplies amino acids required to build peptide messengers like insulin and growth hormone. Studies indicate meals with 25-30 grams of protein reduce hunger signals by 40% compared to low protein options. This occurs through decreased ghrelin production and increased satiety hormones like PYY.
Fiber stabilizes glucose absorption, preventing insulin spikes. Soluble types feed gut bacteria that produce hormones influencing appetite. A 2023 review found high fiber meals improve insulin sensitivity by 25% in adults with metabolic concerns.
Choosing Whole and Unprocessed Foods
Minimally processed options retain nutrients stripped during refining. For example whole grains preserve magnesium and zinc minerals critical for thyroid function. Ultra processed items often contain additives linked to cortisol imbalances.
Focus on ingredients in their natural state: leafy greens, nuts, legumes, and lean meats. These provide synergistic compounds that packaged alternatives lack. One clinical trial showed swapping processed snacks for whole-food alternatives improved estrogen metabolism markers in 8 weeks.
Diet and Hormonal Balance Core Benefits
Strategic food selection serves as your body’s tuning fork for maintaining efficient communication between systems. When meals align with biological needs, they help manage energy distribution while protecting against metabolic strain.
How Balanced Macronutrients Improve Insulin Sensitivity
Protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates work together to stabilize glucose absorption. This trio slows digestion preventing sudden spikes that force cells to ignore insulin signals. Research shows meals combining these elements improve hormone response by 34% compared to carb-heavy options.
| Macronutrient | Impact on Insulin | Optimal Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | Boosts satiety hormones | Lentils, fish, poultry |
| Healthy Fats | Slows glucose release | Avocados, nuts, olive oil |
| Complex Carbs | Provides steady energy | Quinoa, sweet potatoes |
Reducing Sugar and Managing Blood Levels
Added sugars overwhelm your system’s capacity to process glucose efficiently. A 2024 study revealed that consuming 50g of added sugar daily increases insulin resistance markers by 17% within two weeks.
Chronic sugar intake forces the pancreas into overdrive, creating a cycle of rising blood sugar and diminishing cellular response.
Practical strategies for stability:
- Pair fruits with protein to slow fructose absorption
- Choose whole-food snacks over packaged goods
- Read labels for hidden sugars like maltodextrin
These adjustments help cells respond effectively to insulin’s signals, reducing strain on hormone production systems. Over time, this approach supports sustainable energy and metabolic resilience.
Incorporating Protein Rich and Nutrient Dense Foods
Fueling your system with precision nutrients creates a ripple effect across biological processes. Selecting high quality sources ensures your body receives building blocks for cellular repair and efficient signaling.
Essential High Quality Protein Sources
Eggs provide complete amino acids vital for neurotransmitter production. Lean poultry supports tissue growth while stabilizing energy levels. Lentils deliver plant-based protein paired with gut-nourishing fiber.
Fatty fish like salmon supply omega-3s that reduce inflammatory markers linked to insulin resistance. Research shows these fats improve communication between cells, helping regulate appetite signals.
Smart fat choices amplify results. Avocados and nuts contain monounsaturated fats that slow sugar absorption. MCT oil provides instant energy without fat storage triggers. Studies indicate these fats help maintain steady cortisol levels during stress.
Combining these nutrient powerhouses creates meals that sustain energy while supporting metabolic resilience. Consistency matters more than perfection small daily upgrades yield compounding benefits.





