Are you ready to unlock the secrets of the ketogenic diet and transform your health? This high fat low carb lifestyle has gained widespread popularity.
It’s known for its potential benefits, from weight loss to improved blood sugar management. But navigating the dos and don’ts of keto can be a daunting task.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll uncover the science behind ketosis. We’ll explore the essential foods to embrace and shed light on common pitfalls. This will help you for a successful keto journey.
Key Takeaways
- The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate diet. It aims to achieve a metabolic state called ketosis.
- In ketosis, the body breaks down stored fat into molecules called ketone bodies for energy. It uses these instead of blood sugar from food.
- The keto diet typically consists of 5-10% carbohydrates, 70-80% fat, and 10-20% protein.
- The keto diet has been linked to potential benefits. These include weight loss, improved blood pressure, and management of neurological conditions.
- Navigating the keto diet requires a careful balance of essential nutrients. It also means avoiding high-carb foods and beverages.
Understanding the Science Behind Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carb eating plan. It has become popular for its health benefits. At its core is ketosis, where the body uses fat instead of glucose for energy.
What is Ketosis and How Does it Work?
Ketosis happens when you eat very few carbs, less than 50 grams a day. This forces your body to burn fat for energy. It takes a few days to weeks to get into ketosis, depending on how well you stick to the diet.
The Metabolic State of Fat Burning
In ketosis, your body burns fat for energy. It makes ketone bodies, which your brain and other tissues use for energy. This change in how your body uses energy is key to the diet’s benefits.
Daily Macronutrient Ratios
The ketogenic diet has a specific ratio of macronutrients. It’s 55-60% fat, 30-35% protein, and 5-10% carbohydrates. Eating very few carbs 20-50 grams makes your body use fat for energy. Keeping these ratios is important for staying in ketosis.
Ketosis is a metabolic state where the body uses fat as its primary fuel source, rather than carbohydrates.
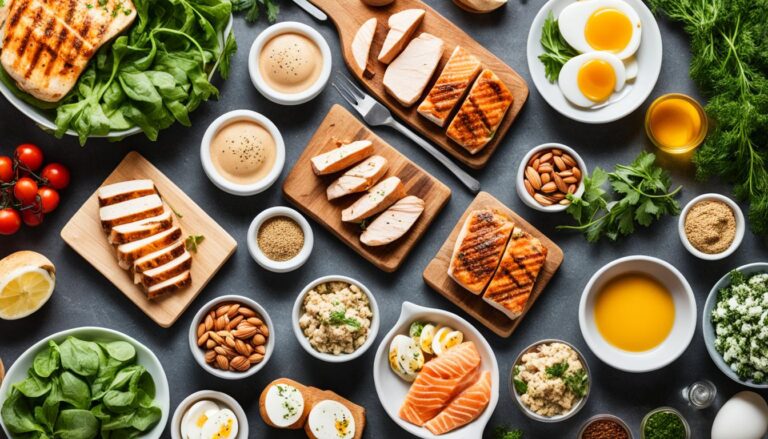
Essential Foods for a Successful Keto Diet
The key to a thriving keto diet is to focus on nutrient-dense, high-fat foods that are low in carbohydrates. These keto-friendly options help keep you in ketosis. They also provide essential vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds. Let’s explore some of the essential foods that should be the foundation of your ketogenic lifestyle.
Seafood and Fish: Fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel are excellent keto foods. They are rich in B vitamins, potassium, and selenium. For example, salmon contains 26g of protein and 11.8g of healthy fats per 100g, with no carbohydrates.
Dairy Products: Cheese, especially cheddar, is a fantastic keto-friendly option. It provides 25.4g of protein, 34.9g of high-fat, and only 0.1g of carbohydrates per 100g. Greek yogurt and cottage cheese are also great choices for their high protein and low carb content.
Avocados and Healthy Oils: Avocados are a versatile low-carb vegetable that boasts 19.7g of healthy fats per 100g, along with 1.9g of protein and carbohydrates. Coconut oil and olive oil are also excellent sources of high-fat nutrition for the keto diet.
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, for instance, contain 16.7g of healthy fats, 8.7g of protein, and only 2.1g of carbohydrates per 100g. They are a perfect keto-friendly snack.
Leafy Greens and Non-Starchy Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, spinach, and bell peppers are all excellent low-carb vegetable options. They are packed with essential nutrients and can be incorporated into a wide range of keto-friendly meals and recipes.
By focusing on these nutrient-dense, high-fat and low-carb foods, you can create a well-balanced ketogenic eating plan. This supports your health and fitness goals.

High Fat Foods to Embrace on Keto
On the ketogenic diet, healthy fats are key. They give you energy, help with hormone production, and improve nutrient absorption. Here are some top high fat foods for your keto diet.
Healthy Oils and Fats
Healthy fats like olive oil, coconut oil, and avocado oil are great for cooking. They’re full of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids. These fats can lower inflammation and boost heart health.
Fatty Fish and Seafood Options
Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are packed with omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3s are good for your brain, reduce chronic disease risk, and improve heart health. Try to eat at least two 3-ounce servings of fatty fish each week.
Nuts and Seeds Selection
Nuts and seeds are great healthy fats for snacks or meals. Good keto choices include almonds, macadamia nuts, walnuts, and chia seeds. Just remember, nuts and seeds have a lot of saturated fats, so watch your portions.
| Food | Carbs g | Fats g | Protein g |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salmon 3 oz | 0 | 4 | 17 |
| Avocado 1 whole | 17 | 30 | 4 |
| Pumpkin Seeds 1 oz | 3 | 14 | 9 |
| Chia Seeds 1 oz | 12 | 9 | 5 |
| Dark Chocolate 3.5 oz, 70% cocoa | 43 | 47 | 7 |
Adding these high-fat foods to your keto diet will give your body the nutrients it needs. It also keeps you in fat-burning ketosis.
Protein Sources for Ketogenic Diet
When you’re on a ketogenic diet, it’s key to get the right amount of protein. The Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health suggests 10 to 20 percent of your daily calories should come from protein. This helps your body get what it needs without kicking you out of ketosis.
Keto protein sources are plentiful. Lean meats like grass-fed beef, chicken, and pork are top choices. Grass-fed beef is packed with iron, zinc, and B vitamins. Pasture-raised eggs are also great, with more omega-3s and vitamins A, E, and antioxidants than regular eggs.
For those who prefer plants, plant-based protein like tofu, tempeh, and nuts and seeds work well. Walnuts, chia seeds, and flax seeds are full of omega-3s. Almonds are a good calcium source.
Fatty fish, like salmon, are perfect for keto protein because they’re rich in omega-3s. These fats are good for your heart and fight inflammation. Turkey is another protein-rich, low-carb choice, offering selenium and vitamin B.
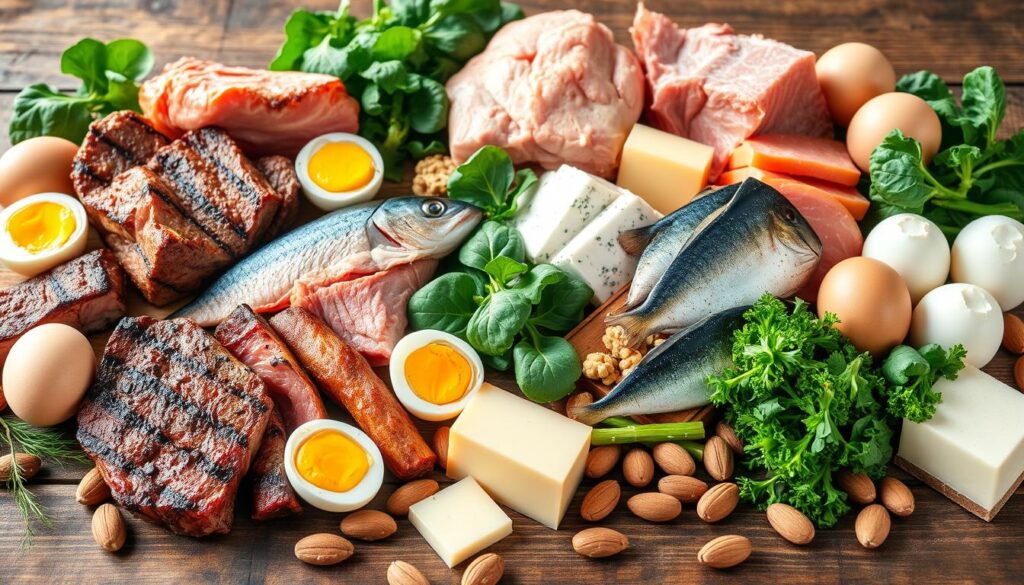

When planning your keto meals, aim for a balance of keto protein and low-carb, high-fat foods. A well-planned keto diet can offer many health benefits. But, always talk to a healthcare expert to make sure you’re getting the right nutrients for you.
Low Carb Vegetables to Include
Following a ketogenic diet means choosing low-carb, fiber-rich veggies. These keto veggies are packed with nutrients and keep your carb intake in check. Let’s look at some top green and non-starchy veggies for your keto meals.
Best Green Vegetables for Keto
- Broccoli 3.5 grams of carbs per 100 grams
- Spinach 3.6 grams of carbs per 100 grams
- Zucchini 3.1 grams of carbs per 100 grams
- Cauliflower 4.97 grams of carbs per 100 grams
- Asparagus 3.88 grams of carbs per 100 grams
- Celery 2.97 grams of carbs per 100 grams
- Cucumbers 3.63 grams of carbs per 100 grams
Starchy Vegetables to Avoid
While keto veggies like the ones above are great, avoid starchier non-starchy vegetables. These include:
- Potatoes 20.45 grams of carbs per 100 grams
- Sweet potatoes 16.82 grams of carbs per 100 grams
- Yams 27.4 grams of carbs per 100 grams
- Corn 18.7 grams of carbs per 100 grams
- Beets 9.56 grams of carbs per 100 grams
Stick to low carb fiber-rich foods and limit starchier veggies. This keeps your keto diet effective and lasting.
Foods to Strictly Avoid on Keto
To burn fat, you need to follow a diet low in carbs and high in fat. It’s key to avoid foods high in high-carb foods, sugar, and processed foods. These keto restrictions help your body stay in ketosis.
Here’s a list of foods to avoid on the keto diet:
- Grains wheat, rice, oats, corn, etc.
- Starchy vegetables like potatoes, sweet potatoes, and corn
- High sugar fruits such as bananas apples, oranges, and grapes
- Sweetened yogurt
- Juices and sugary beverages
- Honey syrup and any form of sugar
- Chips, crackers, and baked goods including gluten-free options
These foods have lots of carbs and can kick you out of ketosis. Always check nutrition labels for hidden sugars in processed foods.
A ketogenic diet typically advises limiting carbohydrate consumption to around 20 to 50 grams per day to achieve and sustain ketosis.
By avoiding these foods, you’re on the path to a successful keto lifestyle.

Ketogenic Diet What to Eat and What to Avoid
The ketogenic diet is all about eating lots of fat, some protein, and very few carbs. Knowing what to eat and what to skip is key to getting into ketosis. This is when your body uses fat for energy instead of carbs and sugar.
For a 2,000-calorie keto diet, aim for 55-60% fat, 30-35% protein, and 5-10% carbs. You should keep carb intake low, around 20-50 grams a day.
Foods to Enjoy on a Keto Diet
- Meat, poultry, and fatty fish
- Eggs
- Butter, ghee, and full fat dairy products
- Nuts, seeds, and healthy oils
- Avocados and low carb vegetables
Foods to Avoid on a Keto Diet
- Sugary foods such as candy, cookies, and soda
- Grains and starches, including bread pasta, and rice
- Legumes beans and most fruits
- Root vegetables, such as potatoes and sweet potatoes
- Unhealthy fats like trans fats and fried foods
- Alcohol, except for dry wines in moderation
- Sugar-free and low carb processed foods
By choosing keto-friendly foods and avoiding high carb items, you can stick to a ketogenic diet plan. This way, you can enjoy the benefits of the keto food list.
The key to success on a keto diet is maintaining the right balance of macronutrients to achieve and sustain ketosis.
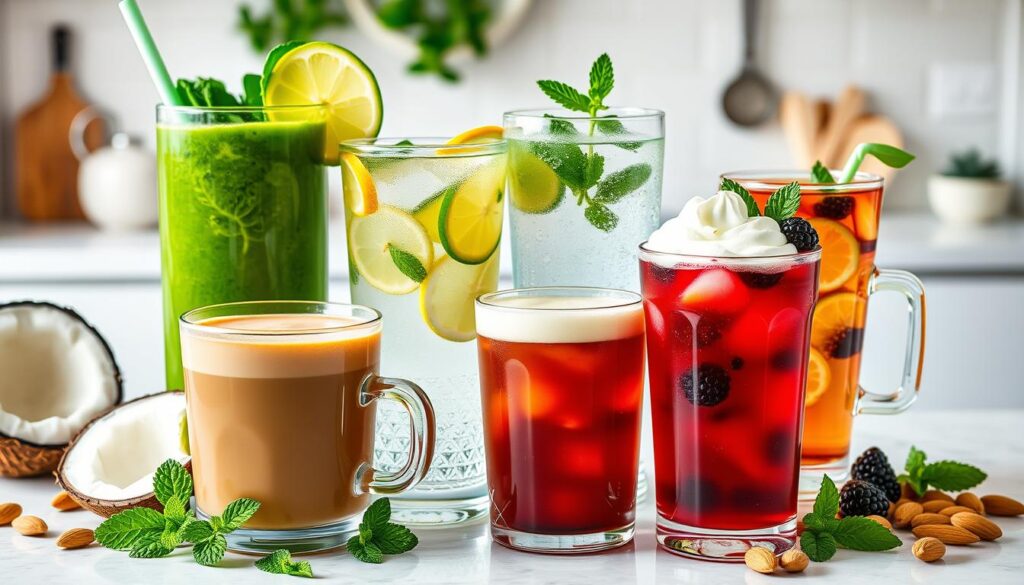
Beverages on the Ketogenic Diet
Staying hydrated is key on a ketogenic diet. The diet’s low-carb nature can make you lose water. Luckily, there are many drinks that keep you hydrated without breaking ketosis.
Acceptable Drinks
- Water – Drinking lots of water is vital for staying hydrated on the keto diet.
- Unsweetened coffee and tea – These drinks have no carbs and can be enjoyed anytime.
- Dry wine and spirits – In small amounts, dry wines and spirits like gin, vodka, and whiskey are okay. They have very few carbs.
Drinks to Eliminate
On a keto diet, it’s crucial to avoid sugary and high-carb drinks. They can mess up ketosis. Here are some drinks to avoid:
- Soda – Regular and diet sodas have too many carbs and should be avoided.
- Fruit juices – Even 100% fruit juices have natural sugars that can stop ketosis.
- Beer – Most beers have a lot of carbs and aren’t good for a keto diet.
Drinking keto-friendly beverages is key to keeping your body in fat-burning mode. It also helps you enjoy the benefits of the ketogenic diet.

Common Mistakes to Avoid When Starting Keto
Starting a ketogenic diet can be a big change. It’s important to watch out for common mistakes to make the transition smoother. Let’s look at some mistakes to avoid on your keto journey.
One big mistake is not eating enough fat. On keto, you should get about 70% of your calories from fat. Not enough fat can stop your body from going into ketosis, where it burns fat for energy.
Another mistake is eating too much protein. While protein is key, too much can turn into glucose, pulling you out of ketosis. Aim for 0.7–0.9 grams of protein per pound of body weight.
Ignoring electrolytes is another common mistake. It can cause the keto flu with symptoms like fatigue and headaches. Make sure you get enough sodium, potassium, and magnesium from foods or supplements.
Lastly, not drinking enough water can make the keto flu worse. Drink at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water a day, especially if you’re active or in a hot place.
Starting keto requires patience and persistence. It can take weeks to adapt, and you might feel the keto flu. Stay hydrated, eat foods rich in electrolytes, and keep going. With the right steps, you’ll see the benefits of a keto diet.
| Common Keto Mistakes | Impact | Recommended Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Not consuming enough fat | Hinders the body’s ability to enter and maintain ketosis | Ensure that 60-75% of your total calories come from healthy fats |
| Eating too much protein | Excess protein can be converted into glucose, disrupting ketosis | Aim for 0.7-0.9 grams of protein per pound of body weight |
| Neglecting electrolytes | Can lead to the keto flu and other unpleasant symptoms | Consume electrolyte-rich foods and, if necessary, supplements |
| Not drinking enough water | Can exacerbate the keto flu and hinder fat-burning adaptation | Aim for at least 8 glasses of water per day, and more if active |
Remember, keto adaptation takes weeks, and the keto flu is common. Stay hydrated, eat foods rich in electrolytes, and keep going. With the right approach, you’ll soon see the benefits of a successful ketogenic diet.
Transitioning into Ketogenic Lifestyle
Starting a ketogenic lifestyle means slowly cutting down on carbs and eating more healthy fats. This helps your body get better at using fat for energy. At first, you might feel tired, have headaches, or feel irritable. These feelings can be lessened by drinking plenty of water, eating enough electrolytes, and making sure you get enough fat.
Adapting to Fat-Based Energy
It usually takes 2-4 weeks to get used to using fat for energy instead of carbs. This change makes your body more efficient at burning fat. To help your body adjust, start by eating fewer carbs and more healthy fats like avocado, nuts, and olive oil.
Managing Initial Side Effects
The keto flu is a common side effect when you first start a ketogenic diet. You might feel tired, have headaches, or feel irritable. To feel better, drink lots of water and eat foods rich in electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium. Adding bone broth, avocado, and salty foods can also help.
By slowly getting used to a keto adaptation and dealing with the first keto transition, you can achieve metabolic flexibility. This makes a ketogenic lifestyle easier and more rewarding.

Tracking Progress and Maintaining Ketosis
Starting a ketogenic diet means you need to track and monitor closely. This is to keep your body in ketosis, a state where it burns fat instead of glucose. It’s about switching from glucose to fat and ketones as the main fuel.
To keep track and stay in ketosis, focus on two main things: macronutrient tracking and ketone testing. Watch your carbs, proteins, and fats. This helps you stay in the right balance for ketosis.
- Aim for 20-50 grams of carbs a day to stay in ketosis.
- Eat plenty of healthy fats like avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
- Keep an eye on your protein to avoid too much gluconeogenesis, which can get you out of ketosis.
Testing your ketone levels regularly is also key. Use urine strips, blood meters, or breath analyzers to check your levels. This helps you adjust your diet as needed.
Tracking your progress and keeping ketosis helps you maintain the keto diet. It’s all about balancing your macronutrients and listening to how your body reacts. This balance is crucial for reaching your health and weight goals.
Conclusion
The ketogenic benefits have caught a lot of attention lately. The diet is now one of the most searched for in the U.S. The keto lifestyle industry is worth over $9.5 billion worldwide. This shows how many people are interested in this diet.
But, it’s important to look at the ketogenic diet carefully. We should see both its good points and the need for long-term health.
The keto diet might help with weight loss, diabetes, and better metabolism. But, it’s not right for everyone. People should talk to doctors to see if it’s good for them. They should also plan a sustainable keto diet that keeps them healthy.
Other diets like the Mediterranean diet can also help with weight and health. They might be better for keeping healthy over time.
Choosing to follow a ketogenic lifestyle needs careful thought. It’s important to get advice from experts. By learning about the diet, making smart food choices, and dealing with any issues, people can enjoy its benefits. They can also keep their health in check for the long run.